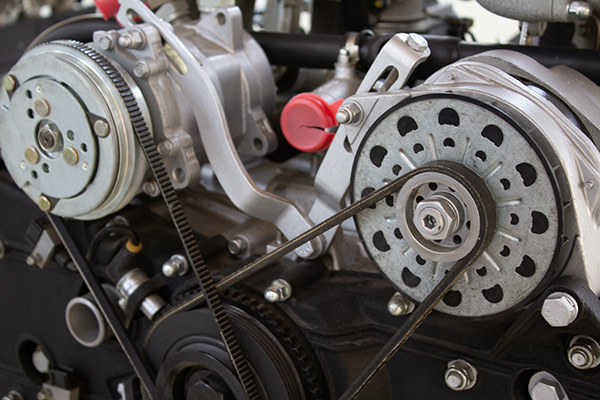
When it comes to the intricate workings of our vehicles, the realm of belts often confuses many drivers. We've all heard of timing belts and serpentine belts, but what exactly sets them apart?
Timing Belt vs. Serpentine Belt
1. Anatomy and Functionality
In the automotive ecosystem, timing belts and serpentine belts play distinct yet equally vital roles. The timing belt, also known as a cambelt or timing chain, is a toothed rubber belt responsible for synchronizing the rotation of the engine's crankshaft and camshaft(s). This synchronization ensures precise valve timing, facilitating efficient combustion and optimal engine performance.
On the other hand, the serpentine belt, aptly named for its snake-like winding path, is a flat, ribbed belt that drives multiple engine components such as the alternator , power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. Unlike the timing belt, which operates internally within the engine, the serpentine belt operates externally, driving various accessories essential for vehicle functionality.
2. Material Composition and Durability
Material composition plays a crucial role in the durability and longevity of timing belts and serpentine belts. Timing belts are typically constructed from reinforced rubber with high-tensile fibers such as fiberglass or Kevlar, ensuring strength and resistance to wear. This robust construction allows timing belts to withstand the rigorous demands of engine operation, providing reliable performance over extended periods.
In contrast, serpentine belts are often made from durable synthetic rubber compounds reinforced with polyester cords. While serpentine belts are designed to endure the stresses of driving multiple engine accessories, they are more susceptible to wear and degradation compared to timing belts due to their external exposure to elements such as heat, oil, and debris.
3. Replacement Intervals and Maintenance
Another significant point of differentiation lies in the replacement intervals and maintenance requirements of timing belts versus serpentine belts. Timing belt replacement intervals typically range from 60,000 to 100,000 miles or every 5 to 7 years, depending on the vehicle manufacturer's recommendations. Failure to replace the timing belt within the specified interval can lead to catastrophic engine damage, making timely replacement crucial for engine longevity and performance.
In contrast, serpentine belts generally have longer replacement intervals, ranging from 50,000 to 120,000 miles. However, it is important to inspect the serpentine belt regularly for signs of wear, such as cracking, fraying, or glazing, and replace it promptly if any abnormalities are detected. Routine maintenance, including belt tension checks and pulley inspection, can help prolong the lifespan of both timing belts and serpentine belts.
Ready to ensure your vehicle's belts are in top-notch condition? Trust LightHouse Automotive for expert belt inspection, replacement, and maintenance services. Book your appointment today and drive with confidence!





.jpeg)



